- Home
- Blog
- Cannabis 101
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS): What is It & How Does It Work?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. Recognized as a crucial modulatory system in the function of the brain, endocrine, and immune tissues, it also plays a fundamental role in the secretion of hormones related to reproductive functions and response to stress.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
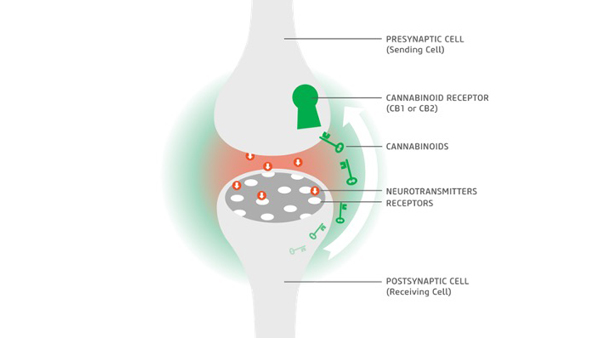
The endocannabinoid system is a network of cannabinoid receptors spread throughout the body. It includes CB1 receptors, mainly present in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2 receptors, found in peripheral organs and cells associated with the immune system. This system is active in your body even if you don't use cannabis and interacts with naturally occurring endocannabinoids that your body produces.
What are Endocannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found within the human body. They are integral to the endocannabinoid system (ECS), playing a pivotal role in maintaining internal homeostasis by regulating various physiological and cognitive processes. These processes include mood, hunger, pain sensation, and memory. Structurally similar to the cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, such as THC and CBD, endocannabinoids interact with cannabinoid receptors throughout the body to trigger various responses aimed at achieving equilibrium.
The two most studied endocannabinoids are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). Their production is on-demand, meaning they are synthesized as needed, unlike many other molecular signals in the body that are produced and stored for later use. Understanding endocannabinoids and their functions help underscore the profound impact the endocannabinoid system has on our overall health and wellbeing.
What Does the Endocannabinoid System Do?
The endocannabinoid system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating a wide range of functions, including sleep, mood, appetite, memory, reproduction, and pain sensation. It does so through the production and breakdown of cannabinoids, which interact with cannabinoid receptors. This interaction stimulates various physiological responses aimed at maintaining balance within the body.
How Does the Endocannabinoid System Work?
The endocannabinoid system works by producing endocannabinoids in response to changes in our internal environment. These endocannabinoids then bind to cannabinoid receptors to signal the ECS to take action. Once the endocannabinoids have done their job and brought things into balance, enzymes break them down to prevent overcorrecting. This process ensures that the internal environment remains stable and operating optimally.
Why is the Endocannabinoid System Important?
The importance of the endocannabinoid system lies in its role in maintaining homeostasis. By regulating a broad spectrum of physiological processes, the ECS ensures that the internal environment of the body is stable and remains within a narrow range of operating conditions, despite changes in the external environment. This balance is crucial for health and well-being, highlighting the endocannabinoid system's significance in the human body.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Endocannabinoid System
How Can You Naturally Stimulate the Endocannabinoid System?
You can naturally stimulate the endocannabinoid system through exercise, diet, and reducing stress. Activities like running, yoga, and any form of regular exercise can increase endocannabinoid levels in the body. Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and reducing stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques can also support ECS health.
What's the Difference Between Cannabinoids and Endocannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis plants, such as THC and CBD, which can interact with the endocannabinoid system. Endocannabinoids, on the other hand, are cannabinoids produced naturally by the body. Both types of cannabinoids can bind to cannabinoid receptors and influence the ECS but come from different sources.
Does Everyone Have an Endocannabinoid System?
Yes, every mammal, including humans, has an endocannabinoid system. It is a fundamental part of our physiology and plays an essential role in maintaining homeostasis, regardless of whether or not one has used cannabis.
When was the Endocannabinoid System Discovered?
The endocannabinoid system was discovered in the early 1990s during research on THC, which led to the identification of cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids. This breakthrough offered profound insights into how cannabis interacts with the body and opened new avenues for understanding human physiology.
Keep Up with Cannabis and Physiology with the Zen Leaf Blog
Eager to learn more about cannabis and how it interacts with your body? Stay tuned in with the Zen Leaf blog! We're dedicated to exploring the fascinating aspects of the plant and, like you, are constantly learning about it. New research is becoming more readily available, all of which we're eager to share with you.b
Our team of authors is not just a group of writers; they are dedicated cannabis experts and pharmacists with years of experience in the industry. Each member brings a unique perspective, combined with a deep understanding of cannabis' therapeutic benefits, emerging research, and regulatory landscape.
Related articles
What are Electronic Dab Rigs & How Do They Work?
Elevate your dabbing with an electronic dab rig, a modern, portable device designed to vaporize cannabis concentrates with precision and convenience.
